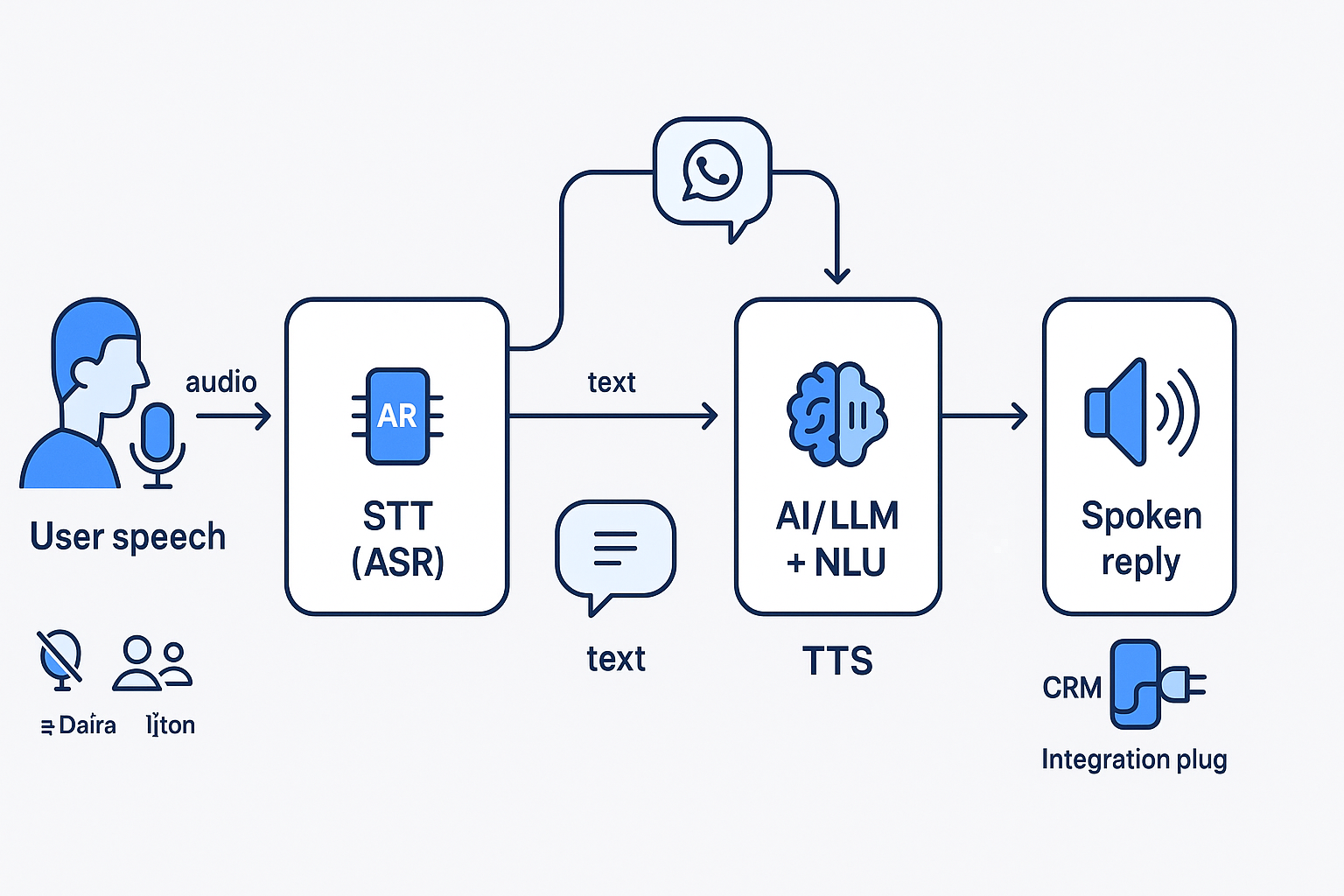
In the rapidly evolving world of AI-driven communication, technologies like Speech-to-Text (STT) and Text-to-Speech (TTS) form the backbone of seamless, human-like interactions. These tools enable AI agents to understand spoken language and respond naturally, powering everything from virtual assistants to customer support systems. At TringTring.ai, our omni-channel AI agents leverage these technologies to handle voice calls, WhatsApp messages, and social interactions with remarkable efficiency. In this post, we’ll break down STT and TTS, highlight their differences, and explain how they integrate into the AI voice pipeline for real-world applications.

What is Speech-to-Text (STT)?
Speech-to-Text, also known as automatic speech recognition (ASR), converts spoken language into written text. This technology is crucial for enabling AI systems to “hear” and process human speech in real-time or batch modes.
How STT Works: Pipeline Steps
The STT process involves sophisticated models that analyze audio signals:
- Audio Input: Captures speech from microphones, files, or streams.
- Preprocessing and Feature Extraction: Analyzes sound waves, identifies phonetic components, and extracts features like frequencies.
- Recognition and Transcription: Uses deep learning models (e.g., RNNs or Transformers) to match audio to words, considering grammar, context, and dialects.
- Output: Produces text, often with punctuation, speaker diarization (identifying multiple speakers), or custom adaptations for noisy environments.
Advanced systems like Azure AI Speech handle real-time, fast, or batch transcription, with custom models for domain-specific accuracy (e.g., medical or legal terms).
Applications of STT
- Voice assistants (e.g., Siri, Alexa) for commands and queries.
- Transcription services for meetings, podcasts, and videos.
- Customer service for real-time call analysis.
- Accessibility tools for the hearing impaired, like live captioning.
At TringTring.ai, STT powers our AI agents to transcribe incoming voice queries accurately, even in noisy settings, ensuring reliable sales and support interactions.
What is Text-to-Speech (TTS)?
Text-to-Speech, or speech synthesis, does the opposite: it converts written text into natural-sounding spoken audio. Modern TTS uses AI to mimic human intonation, making interactions feel lifelike.
How TTS Works: Pipeline Steps
Neural TTS, the state-of-the-art approach, involves:
- Text Input: Receives text, often enhanced with SSML (Speech Synthesis Markup Language) for customization.
- Linguistic Analysis: Breaks down grammar, prosody (stress and intonation), and context.
- Synthesis: Deep neural networks generate spectrograms (sound visuals) and convert them to audio waveforms.
- Output: Produces high-quality speech, customizable for pitch, speed, or voice.
Systems like Azure’s neural TTS predict prosody and voice simultaneously for reduced listening fatigue, supporting real-time or asynchronous synthesis for long content.
Applications of TTS
- Voice assistants for verbal responses.
- Audiobooks and e-learning narration.
- Navigation systems for spoken directions.
- Accessibility for the visually impaired, reading text aloud.
TringTring.ai uses TTS to deliver human-like responses across channels, enhancing user engagement in sales calls or support chats.

STT vs TTS: Key Differences
While both are essential for voice AI, STT and TTS serve opposite roles in the communication loop. Here’s a comparison:
| Aspect | Speech-to-Text (STT) | Text-to-Speech (TTS) |
|---|---|---|
| Direction | Audio to text | Text to audio |
| Core Function | Transcription and recognition | Synthesis and voice generation |
| Pipeline Focus | Feature extraction, phonetic analysis | Prosody prediction, waveform generation |
| Challenges | Handling accents, noise, dialects | Achieving natural intonation, emotion |
| Applications | Dictation, captions, voice commands | Narration, assistants, announcements |
| AI Models | Transformers, RNNs for accuracy | Neural networks for realism |
STT is input-centric, focusing on understanding, while TTS is output-driven, emphasizing delivery.

The AI Voice Pipeline: How STT and TTS Work Together
In a complete AI voice system, STT and TTS form a unified pipeline, often called the STT → LLM → TTS flow:
- User Input: Speech is captured and sent to STT for transcription.
- Processing: The text is analyzed by an AI model (e.g., LLM like GPT) to generate a response, incorporating NLP for context and intent.
- Output: The response text is fed to TTS for spoken audio delivery.
This pipeline enables real-time conversations with low latency (under 500ms for optimal flow). Emerging speech-to-speech (STS) models merge these steps for even faster, more natural interactions, preserving tone and emotion.
For TringTring.ai, this pipeline powers our AI agents to handle complex queries across voice and text channels, integrating with CRMs for personalized responses.
TringTring.ai’s Approach to AI Voice Pipelines
At TringTring.ai, we optimize the STT-TTS pipeline for omni-channel efficiency. Our agents use advanced STT to transcribe calls in real-time, process them with AI for intelligent replies, and employ TTS for natural, customizable voices. This setup supports use cases in real estate, finance, and healthcare, where quick, accurate communication drives results. With pay-per-minute pricing and seamless integrations, TringTring.ai makes deploying voice AI straightforward and scalable.
Conclusion
STT and TTS are not just tools—they’re the foundation of interactive AI. By understanding their roles and integration in the voice pipeline, businesses can unlock more engaging customer experiences. As AI evolves, expect even more seamless, multimodal systems. Ready to implement this in your operations? Explore TringTring.ai’s features today and see how our AI agents can transform your sales and support.
Published on [Date]. For more insights on AI agents, check out our use-cases page.
Would you like me to generate the images for this blog post? Here are the suggested prompts for optimization (e.g., high-resolution, SEO-friendly alt texts, compressed for web):
- “Create a clean, illustrative diagram of the AI voice pipeline showing user speech input, STT conversion to text, AI/LLM processing, TTS conversion to speech, and output response. Use blue tones for a tech feel.”
- “Generate a step-by-step flowchart for the Speech-to-Text (STT) process, including audio input, preprocessing, recognition, and text output. Simple icons and arrows.”
- “Design a flowchart for the Text-to-Speech (TTS) process, depicting text input, linguistic analysis, synthesis, and audio output. Include neural network elements.”
- “Make an infographic comparing STT and TTS with icons, bullet points for differences, and a versus symbol in the center. Modern and colorful design.”